In the narrow space of earthquake ruins, the carbon dioxide exhaled by survivors is enriched, and survivors can be searched through the CO2 volume fraction test. To this end, a carbon dioxide detection device designed for use on the site of a rubble was designed. Currently widely used carbon dioxide sensors include solid electrolyte sensors, infrared sensors, and the like. The solid electrolyte carbon dioxide sensor is a hybrid type carbon dioxide sensitive element with a built-in thermistor. Its advantages are small size and insensitivity to environmental temperature and humidity. Disadvantages are the long warm-up time, generally 2 hours to achieve stability, therefore, is not suitable for equipment used in the field. This design adopts a non-dispersive infrared carbon dioxide sensor with no moving parts inside and no chemical reaction in the measurement process. The sensor has the characteristics of wide measurement range, high sensitivity, fast response time, good selectivity, and strong anti-interference ability. JIS B 8241 Steel Gas Cylinders 3L Activated Cylinder,5L Activated Cylinder,3L Fire Extinguishing Activated Cylinder Hangzhou Tianlong Steel Cylinder Co., Ltd. , http://www.hzgascylinder.com
1 Working principle The infrared absorption spectrum of carbon dioxide is shown in Fig. 1. At a wave number of 2 342 cm-1, carbon dioxide has a strong absorption peak. The absorption relationship obeys the Lambert-Beer absorption law. The relationship between the intensity I of the exiting light, the intensity I of the incident light, and the volume fraction C of the gas is I = I0exp( εLC). (1) where ε is the mole Absorption coefficient; C is the volume fraction of the gas to be measured, L is the length of the light and gas (length of light path). The above equation is converted to C = 1 εLln (I0/I). (2) When the molar absorption coefficient is fixed, the volume fraction of carbon dioxide can be calculated by detecting the intensity of the emitted light. Due to different molecular structures of gas molecules, their absorption peak positions are also different. Using infrared light with a wave number of 2342 cm-1 as a light source to detect carbon dioxide volume fraction is not easily affected by the concentration of other gas molecules. However, the molar absorption coefficient is influenced by the ambient temperature and pressure, and the gas density decreases as the temperature increases, and the measured volume fraction decreases. As the gas pressure increases, the gas density increases, and the measured volume fraction rises. Therefore, the measurement result of the infrared carbon dioxide sensor needs to be corrected. .
2 system design 2. 1 hardware circuit design system hardware structure shown in Figure 2. MCU selects STC 12C5A60S2, pin connection is shown in Figure 3. 12C5A60S2 is a new generation of 8051 microcontroller with high speed, low power consumption, super anti-interference, operating voltage range of 5. 5 ~ 3. 3 V; operating frequency range is 0 ~ 35 MHz, equivalent to 0 to 420 MHz for normal 8 051; 1 280 B on-chip RAM data memory; 4 16-bit timers.
Fig. 1 Infrared absorption spectrum of carbon dioxide 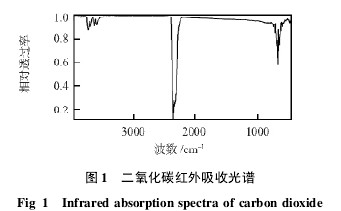
The microcontroller supports two full-duplex asynchronous serial ports (UARTs) for CO2 volume fraction acquisition and data display.
Figure 2 System hardware structure 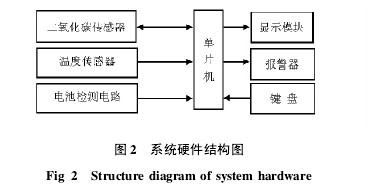
Figure 3 Microcontroller pin connection schematic 
The use of GE's infrared CO2 sensing module Telaire 6004 with a range of 0% to 1% as the detection unit, optical path, signal conditioning, and A/D conversion is completed within the module. The measurement results are communicated with the microcontroller using the UART serial interface, effectively avoiding external The effect of electromagnetic interference on the measurement. Digital temperature sensor DS18B20 is used as a temperature measuring element, and temperature compensation is achieved through a program. The system uses 2 Ah lithium batteries as the power supply. The A/D conversion provided by the microcontroller is used to measure battery power. When the battery is low, an alarm occurs. According to actual measurement, it can work continuously for 6 hours to meet field work requirements.
The display module adopts a vacuum fluorescent display (VFD), which uses electrons to hit the phosphor to make the phosphor emit light. Compared with the traditional LCD and LED displays, the display module has a wide range of temperature adaptation, high brightness, and is still exposed to strong outdoor light. Clear readings. Therefore, the VFD display is suitable for field work instruments.
2. 2 software design SCM control software uses a modular design, using C language, the main program flow shown in Figure 4. First initialize the system configuration, serial port 1 receives the output of the CO2 module, and serial port 2 sends the display data. Press the key to enter the altitude, the table value method to obtain the pressure value. The single-wire bus reads the temperature value measured by the DS18B20, and the microcontroller ADC0 reads the battery voltage. Read the CO2 volume fraction value and send it to the screen for temperature and pressure correction. The pressure correction relationship is based on 1013 hPa, with 0.1% increase in measured value per 1hPa, 0.1% decrease in measured value per 1hPa, and a temperature correction relationship of 22°C as the reference value, for every 1°C increase. The measured value is reduced by 20 × 10 - 6 and the measured value is increased by 20 × 10 - 6 for every 1 °C decrease. The corrected measurement result is compared with the preset value. If the carbon dioxide volume fraction is higher than the preset standard, it indicates that there may be survivors. The system will issue a sound and light alarm. Otherwise, it will enter the loop detection.
Figure 4 software flow chart 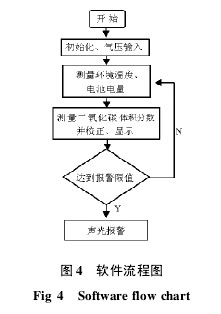
3 Experiment The repeatability of the CO2 detector was 0.6%, and the uncertainty was 1.5%. It has been used in survivor search simulations. In the experiment, a subject entered a narrow space of about 6m3, the space ventilation area was about 0.02m2, the ventilation speed was 0.2m/s, and the outside space carbon dioxide volume fraction was 800×10-6. The space carbon dioxide volume fraction change was shown in Figure 5 . Experiments show that the breathing of survivors in a narrow space can increase the volume fraction of carbon dioxide in the space.
Fig. 5 Results of detection of carbon dioxide volume fraction in the narrow space of subjects 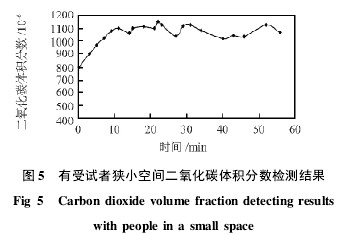
4 Conclusion The narrow space of earthquake ruins may enrich the carbon dioxide exhaled by survivors. By detecting the volume fraction of carbon dioxide in the ruins, it can be used as a method to search for survivors. A portable carbon dioxide volume fraction detector was designed for this purpose. The 12C5A60S2 microcontroller was used as a control unit, and a digital infrared carbon dioxide sensor was used to perform temperature and pressure correction. The instrument does not require external AC power supply and has good temperature adaptability. The experimental test of the simulated debris shows that: The designed carbon dioxide detector is reliable and adaptable to the environment, and is suitable for survivors searching on the site of earthquake ruins.
Design of portable carbon dioxide detection equipment