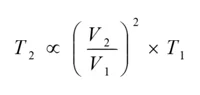Troubleshooting Basics: Motor Noises
Motors make noise. The key is to know how to distinguish normal from abnormal sounds and how to troubleshoot them effectively.
Like a baby, a motor doesn't communicate when it's having problems or what you need to do, but the sound it makes can give you valuable clues.
If a motor produces unusual noise, possible causes may include:
- Backlash
- Gear issues
- Excessive vibration
- Motor damage
- Gearhead damage
This article explores these types of noises and offers solutions to reduce them. It’s important to isolate the motor from other noise sources like metal plates or loose bolts. Having an extra motor in good condition for comparison can also be very helpful as a reference point.
For more information, continue reading.
Backlash
Noise in geared motors often comes from the continuous collision of gear surfaces inside the gearhead during rotation. This is due to backlash, which is the space between gear teeth. This sound usually resembles a consistent "hum" and can vary depending on the type of gears used. However, this noise does not necessarily indicate a malfunction and won’t affect the motor’s performance or the gearhead’s lifespan.
We provide an example using a spur gear with backlash.
In some cases, this backlash noise can become louder, especially if the motor is unloaded or oversized. For AC motors, when the load is lighter than the rated load, the motor isn't operating at its optimal efficiency, leading to increased vibration and noise. When the motor reverses direction, the backlash might cause different impact noises between gears. Brushless and stepper motors don’t face this issue because their drivers regulate power effectively.
How to Verify?
This noise is typically louder when the motor is unloaded or oversized. If applying a light frictional load to the gearhead output shaft reduces the noise, then it's likely normal. If increasing the load doesn’t help or increases the noise, or if the noise is inconsistent, it could be caused by something else. In bi-directional applications, using helical gears or higher-quality gears with more contact surface area can help reduce impact noise. For optimal performance, a motor sizing consultation should include selecting the right motor and gear type.
| FYI |
|
AC motors perform best under their rated load since all mechanical and electrical specs were designed for that load. An unloaded motor tends to be noisier than one with a rated load. For brushless motors, oversizing is less of an issue because they only draw as much current as needed. For stepper motors, even if oversized, reducing the current setting can lower torque and minimize vibration. |
Gears
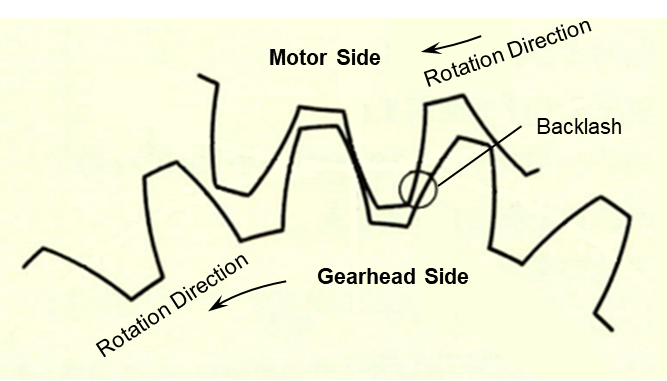
In geared motors, gears are always meshing with each other. Any damage or scratches on the gear teeth can cause abnormal noise during rotation. If you notice increased noise after assembling or disassembling the motor and gearhead, it might mean the gear teeth were damaged or scratched.
To keep the design compact, Oriental Motor doesn't use a coupling between the motor shaft and gearhead. Instead, the motor shaft is machined into a pinion shaft, which directly mates with the internal gears in the gearhead, as shown below (motor shaft is on the right side).

Since the motor's pinion shaft directly mates with the gears, any scratch or damage on the pinion shaft can lead to additional noise. Fortunately, this doesn't affect the motor's performance, although there's no easy fix for it.
How to Verify?
If the noise level is significantly higher when the motor and gearhead are assembled compared to just the motor, it may indicate damage or scratches on the gear teeth. Unfortunately, the only solution is to replace the gearhead.
If you hear a periodic sound at specific intervals, it might help identify which gear tooth or side is damaged. Oriental Motor can inspect the product to confirm tooth damage, but there's little else we can do.
| FYI |
| When assembling or disassembling gearheads from motors with a pinion shaft, be cautious to avoid damaging the internal gears. Follow the installation instructions in the manual. If you're unsure, consider purchasing pre-assembled options. |
Excessive Vibration
Vibration contributes to noise. One factor that can increase motor vibration is incorrect wiring or power supply voltage. Higher voltage increases torque, but excessive torque can amplify noise. Voltage fluctuations also affect the motor's speed-torque curve and operating temperature. Vibration can be amplified through other means, such as loose bolts or metal plates. When troubleshooting noise, it's essential to isolate all other vibrations.
How to Verify?
Check the wiring between the power supply, capacitor, and motor, and ensure the input voltage is within +/-10% of the motor's specifications. Also, verify that the correct capacitor is connected between the power supply and the motor. The voltage and capacitance of the capacitor are crucial in determining the motor's speed-torque curve, rated torque, and magnetic balance. Using the wrong voltage or capacitance can reduce efficiency and increase vibration.
Here’s how a voltage tester can be used.
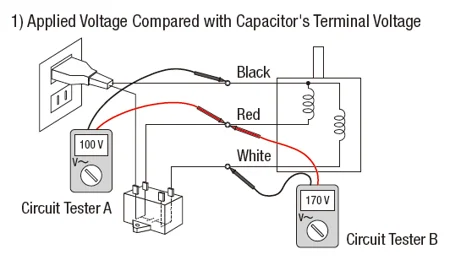
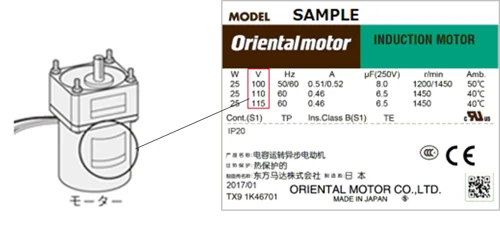
A voltage approximately 1.4 to 1.7 times higher than the power supply voltage is applied across the capacitor pins. The capacitor's rated voltage differs from the motor's. For instance, if the motor's rated voltage is 100 VAC, the capacitor's rated voltage might be 250 VAC or higher.
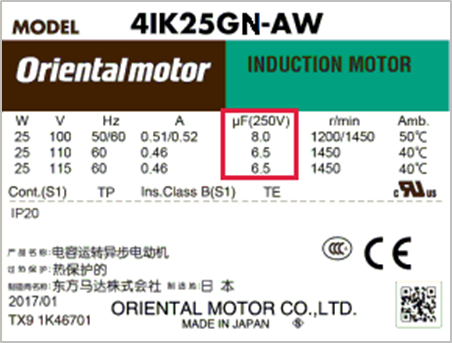
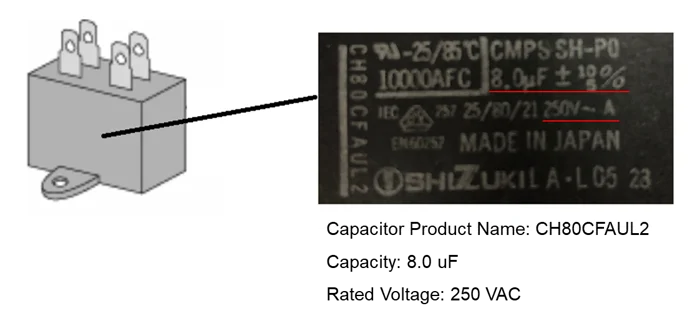
The capacitance specification is listed on the motor label and the capacitor (as well as our website, catalogs, and brochures). In the example below, a single-phase 100 VAC induction motor uses an 8 microfarad capacitor. The same motor operates at 115 VAC with a 6.5 microfarad capacitor. The capacitor's rated voltage is 250 VAC.
| FYI |
|
For AC motors: Ensure the input voltage is within +/-10% of the specification. Torque changes with voltage fluctuations. The motor’s torque is roughly proportional to the square of the input voltage.
A low input voltage may result in insufficient torque. A higher input voltage may increase torque but also raise temperature and vibration. For brushless motors: Drivers regulate voltage and current according to the load, minimizing excessive vibration. For stepper motors: If excessive vibration occurs due to high torque, reduce the driver's current setting or use a smaller motor. A motor sizing consultation is recommended. |
Motor Damage
If the motor shaft makes noise without the gearhead, there's likely an issue with the motor. For example, the motor bearing may be damaged by excessive load. Sometimes, mishandling, like dropping the motor, can also cause damage.
How to Verify?
Disconnect the motor from power and load. Visually check the pinion shaft for damage and try rotating the motor shaft forward and backward by hand. If you can't rotate it fully, the bearings might be damaged. For motors with an electromagnetic brake, ensure it's released before testing. Some pre-assembled motors, like stepper motors, cannot be disassembled. In such cases, replacement is necessary.
| FYI |
|
If you can't manually rotate the motor's pinion shaft clockwise or counter-clockwise, or if it makes an abnormal noise while doing so, the motor bearing is likely damaged. Since our motor case is not designed to be opened, there's no easy way to repair bearing issues. Please purchase a new motor and take preventive measures. |
Gearhead Damage
If the gearhead makes noise without the motor, it's likely damaged. This could involve the gearhead case, bearings, or gears. Troubleshooting without a reference point or accurate measurement is challenging.
How to Verify?
Similar to checking the motor bearing, remove the gearhead from the motor and visually inspect the gears. Some internal gears will be visible once the gearhead is removed. You can try rotating the gearhead shaft to inspect more gears. Shaking the gearhead should not produce a "loose" sound. Try rotating the gearhead shaft forward and backward by hand, though this may be difficult depending on size and gear ratio.
| FYI |
| If the gearhead makes an irregular cyclical noise or you can't turn the output shaft manually, it indicates either certain gears or the bearings are damaged. Please replace the gearhead. |
That’s it for now! The easiest way to fix these issues is to replace the motor and/or gearhead. A better approach is to prevent them by performing a motor sizing analysis. This article provides deeper insights into motor noise for those interested in learning more and avoiding similar issues in the future.
Feel free to reach out to our technical support team via phone, email, or chat for further assistance.
FAQs
|
Q: I bought the same motor and gearhead as before, but the noise during operation is louder than the ones I used before. What could be the reasons? |
|
A: Possible causes include: (1) The gearhead's backlash sound varies with load conditions. For example, without a load, the gears bounce during rotation, causing continuous collisions and noise. Adding a friction load can suppress this sound. (2) Resonance in the workpiece might be amplifying the noise. Check the load conditions and mounting method. (3) Scratches on the motor shaft. During assembly or due to overloading, the gear teeth may get scratched, causing noise. Use spigot parts as guides during assembly and gently rotate the gearhead to avoid damaging the teeth. |
| Q: How do I replace a gearhead of a combination type (pre-assembled geared motor)? |
|
A: Follow the manual's instructions for disassembly and assembly, including tightening torque. ・Do not force the motor and gearhead together, or insert foreign objects like metal pieces inside the gearhead. Doing so may damage the pinion or gear of the motor output shaft, resulting in abnormal noise or shortened service life. ・Ensure the motor and gearhead spigots are clean and free from dust. Be careful not to trap the O-ring on the motor's spigot. Doing so may cause grease leakage from the gearhead. ・Use the included hexagon socket head bolt set for installation. These bolts are for fixing the motor and gearhead. |
| Q: How do I check if specific motors and gearheads can be combined? |
| A: Check the part number description or look up compatible gearheads. You can also ask our technical support engineers for quick guidance. |
| Q: Is there a way to check if the AC motor is broken? |
| A: Yes, there are three ways.
1. Measure the motor winding resistance to check the winding state <Caution> ・Before checking, make sure to turn off the power to prevent electric shock and short circuits.・If the breaker trips when power is applied, the motor power line may have a ground fault or the motor may have insulation breakdown. It is recommended to replace the motor capacitor without turning on the power. |
Disclaimer: This article provides troubleshooting tips, but only qualified professionals should perform the work. If you are not qualified, please contact our technical support team. Oriental Motor is not liable for any injuries that may occur from performing the work.
Â
Ceramic Ring Replacement needs to spin off the nozzle first, followed by the Ceramic Ring Lock Master Spin, note that in the process of rotating fingers to resist the old ceramic ring to prevent vertical sliding down. In the replacement of ceramic ring, need to cut the bottom of the copper pillar to the induction hole, normal alignment of good ceramic ring is horizontal, will be a bit elastic, around can not rotate. Then the finger is pressed against the ceramic ring and the locking block, and finally the nozzle is screwed on to complete the installation. At the same time, after the installation is completed, it is necessary to debug the beam path to prevent the deviation of the light.The advantage of Zirconia ceramic ring is its extremely small Coefficient of thermal expansion (high temperature resistance) , high density (wear resistance) , high resistivity. Such a ceramic body can effectively ensure the insulation of important parts and cutting head, and further reduce the loss of cutting head.
Ceramic Body,Corrosion resistance,High temperature resistance,High resistivity
Wuxi huaoulai automation equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.china-hol.com